

Even if you can’t feel yourself sweating, nearly imperceptible changes in skin conductivity can tell scientists a lot about what you’re experiencing. The variation of a low-voltage applied current between the two electrodes is used as measure of the EDA. Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) is a measure of skin conductivity, and is perhaps most well-known as an element of the polygraph (lie-detector) test. The GSR signal is very easy to record: in general just two electrodes put at the second and third finger of one hand are necessary. The galvanic skin response is a negative shift of biopotential or a decrease in electrocutaneous resistance caused by the activity of the sweat glands just before perspiration. Such system is directly involved in the emotional behavioural regualation in the humans.Īdditional studies highlighted the relationship between GSR signal and some mental states, such as stress, drowsiness and engagement. The GSR can be measured using several measurement methods: Electro-physiological measurement like ECG or EMG. Galvanic skin response is usually recorded by measuring the indexes between the palmar and dorsal surfaces of the hand or between the palmar surfaces of both hands.

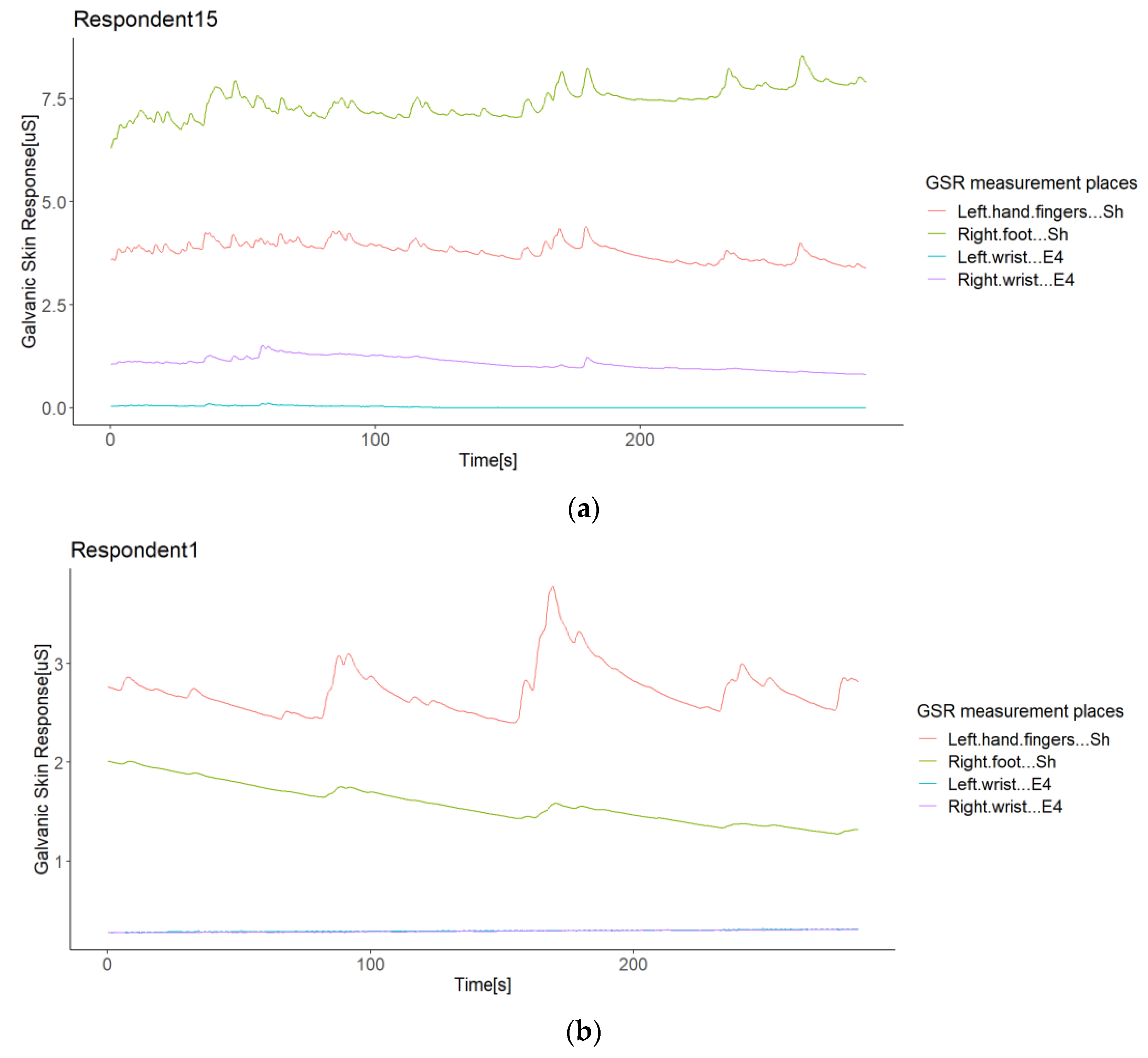
In this way, skin conductance can be a measure of the human Sympathetic Nervous System responses. In particular, if the sympathetic branch ( SNS) of the autonomic nervous system is highly aroused, then sweat gland activity also increases, which in turn increases skin conductance, and viceversa. Human body sweating is regulated by the Autonomic Nervous System ( ANS). The traditional theory of the GSR analysis is based on the assumption that skin resistance varies with the state of sweat glands in the skin.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
